ENGLISH LANGUAGE
context ... formality ... grammar ... graphology ... idiolect ... morphology ... phonology ... semantics
space
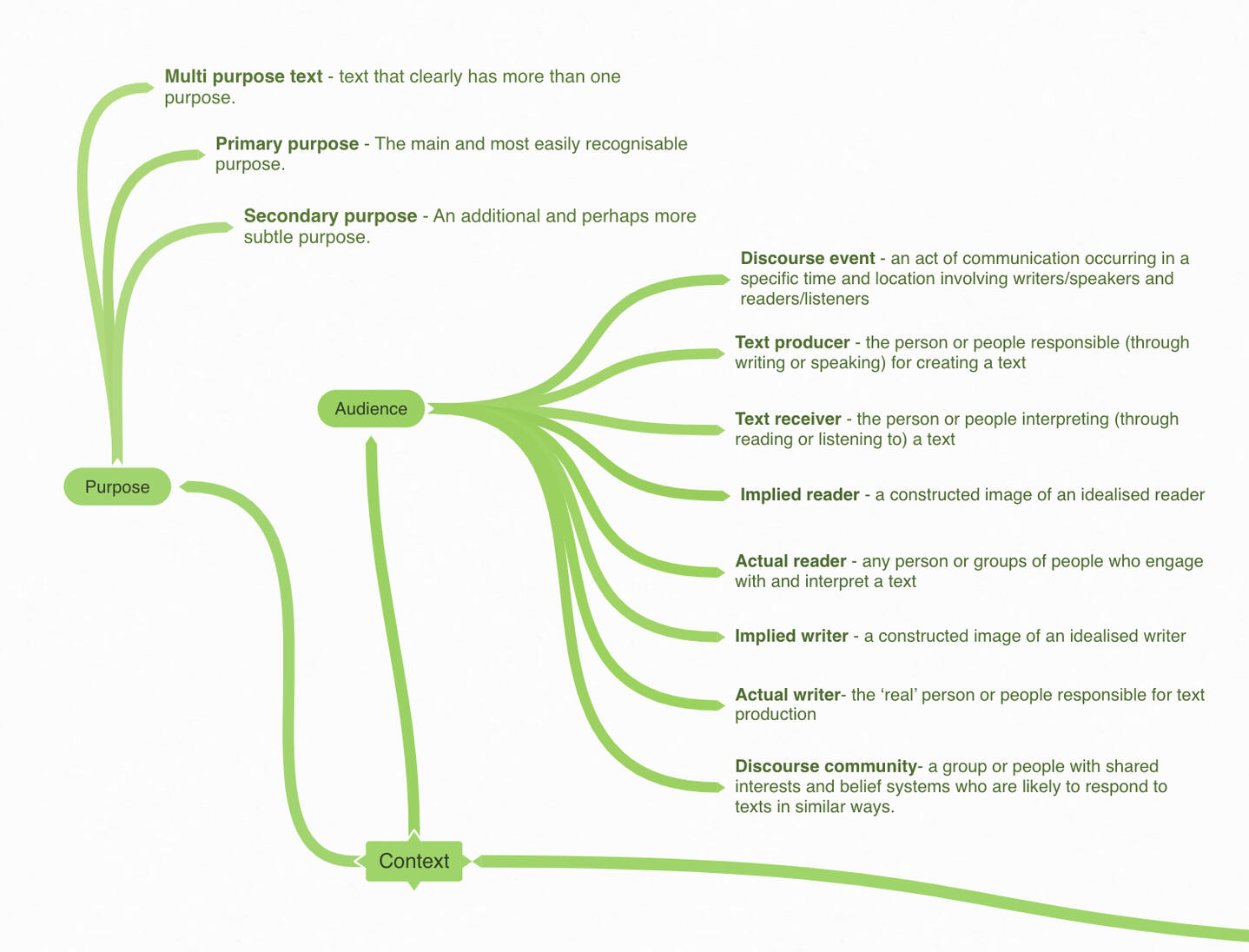
CONTEXT
Every text has a context, like the writer's purpose, intended audience, or historical events, etc.
Regardless of the producer’s original purpose, the impact of the message could be very different from that originally intended. It’s also important to explore what in reality a text gets used for, that is, to think about its function, or use of a text.
FORMALITY
A formality is a thing that is done simply to comply with convention, regulations, or custom.
Formality is important in language because it can show someone's seriousness or respect for their audience and topic.
The formality spectrum is as follows:
taboo
vulgarism
slang
non-standard dialect
colloquialism
informal Standard English
neutral Standard English
formal Standard English
very formal Standard English
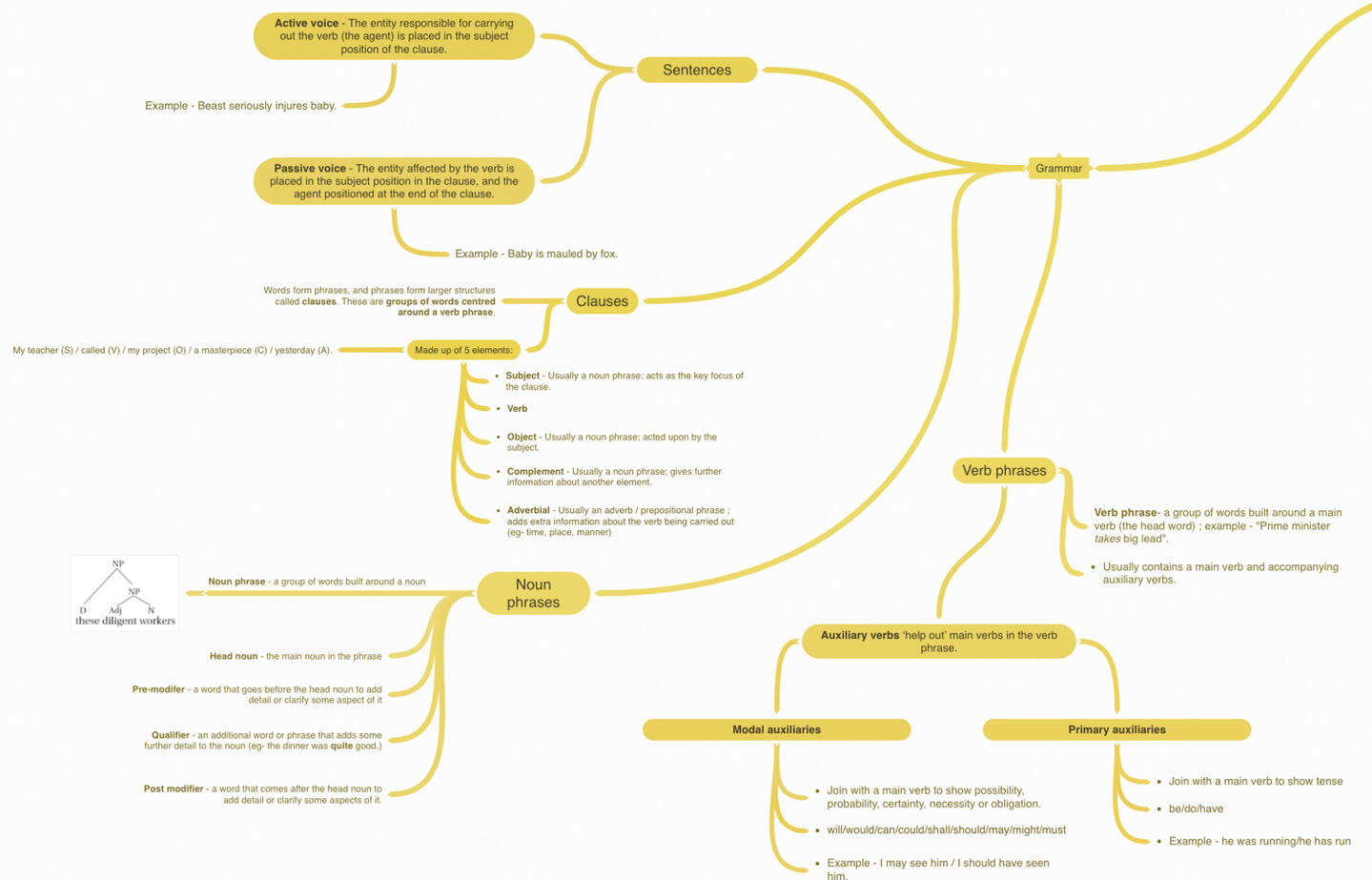
GRAMMAR
GRAPHOLOGY
Graphology is being concerned with the visual elements of a text, both verbal and non-verbal like shape, image, colour, space and typography.
FONT
Sans serif fonts like the one used in this website are considered to be sleek, stable and modern.
Meanwhile, serif fonts like this one feel more traditional, authoritative and respectful. They're often used in legal documents.
COLOURS
For example, red is associated with has danger and passion, while blue is associated with calm and peace. Green is usually used in branding because of associations with nature and healing.
ICONIC AND SYMBOLIC IMAGES
An iconic sign is a sign or image that is a direct picture of the thing it represents. A symbolic sign
a sign or image where an associated meaning is drawn from some shared degree of knowledge.
IDIOLECT
The language used by an individual, expressing themselves in their own style depending on how they have been influenced. This depends on factors like age, gender, education, social class etc.
SOCIOLECT
The language associated with a particular social group.
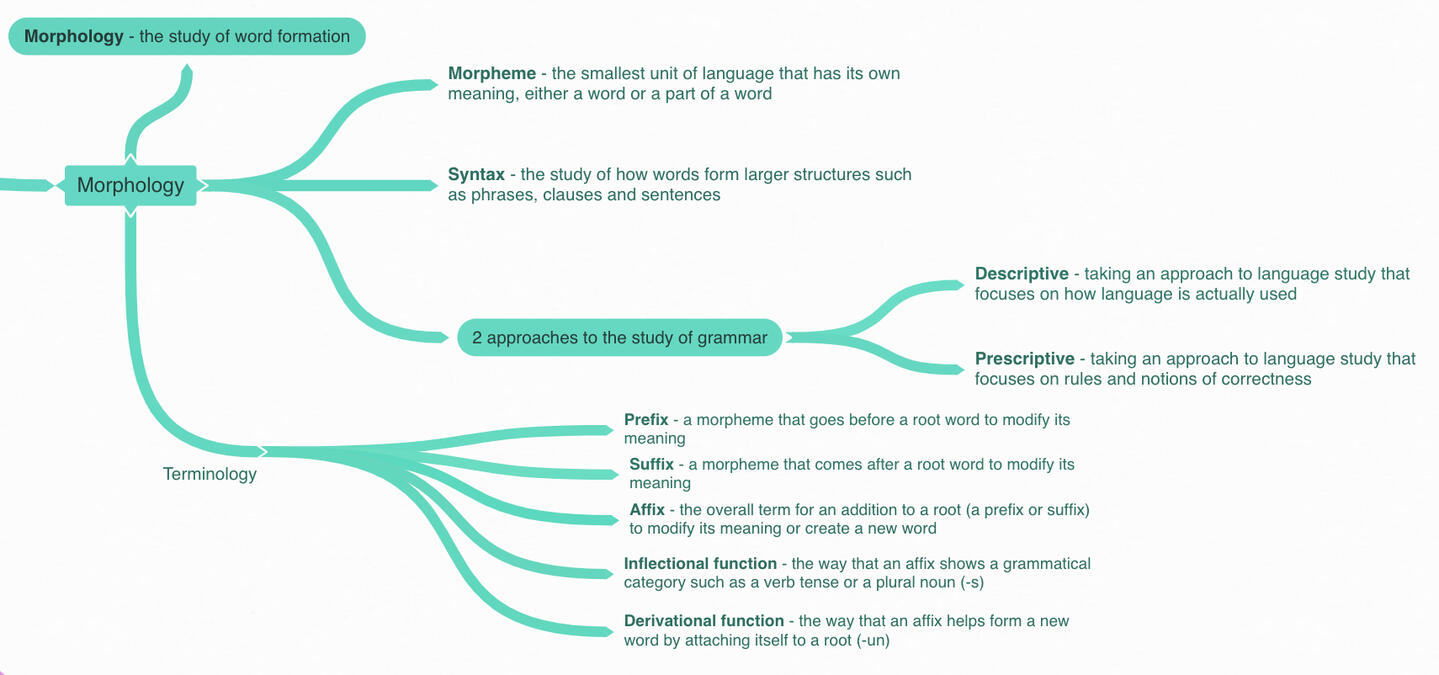
MORPHOLOGY
PHONOLOGY
/fəˈnɒlədʒi/
Phonology is the area of study that refers to the more abstract sound system, like alliteration. Meanwhile, phonetics is the area of study that is concerned with investigating how sounds are actually produced by language users, and involves biology. Lastly, prosodics: the study of how speakers can shape meanings through emphasising certain aspects of intonation, speed and volume.
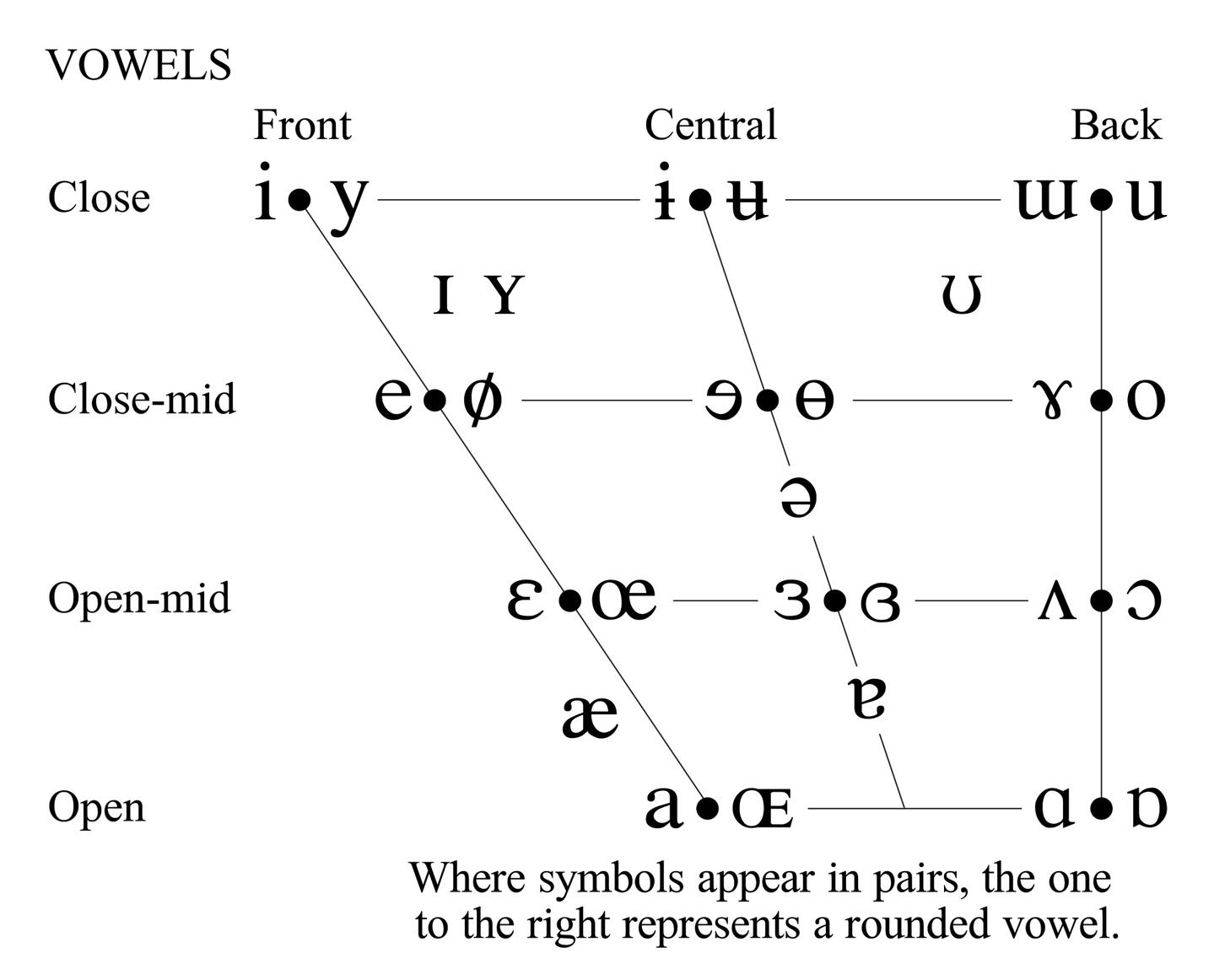
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is a system for showing the different sounds that can be possibly made in the English language.
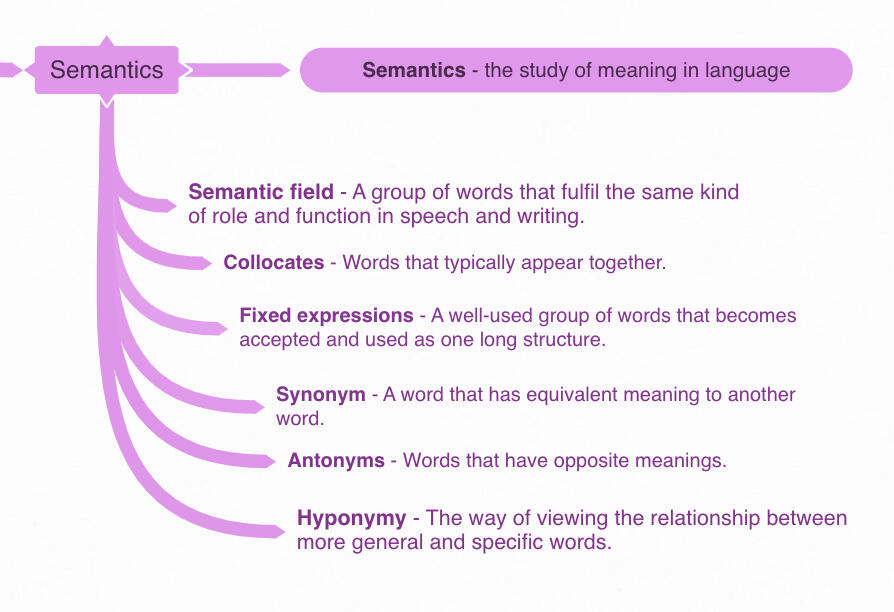
SEMANTICS
Semantics is the study of meaning in language.
There are blurred edges to the meaning of nearly ever word. Meanings depend on context. For example, the word table refers to an item of furniture, usually with four legs, that is used by someone sitting at it to undertake some kind of task, but sometimes the word is extended into a metaphor, like in the headline "Arsenal table bid for French Striker".
There are also two types of synonyms: euphemisms, that use more socially acceptable words or phrases, and dysphemisms, that use a blunt or direct word that is close to taboo.